Note:
If you guys are getting coupon expired or course is not free after opening the link, then it is due to the fact that course instructors provide only few hundreds or thousands of slots which get exhausted. So, try to enroll in the course as soon as it is posted in the channel. The Coupons may expire any time for instant notification follow telegram channel


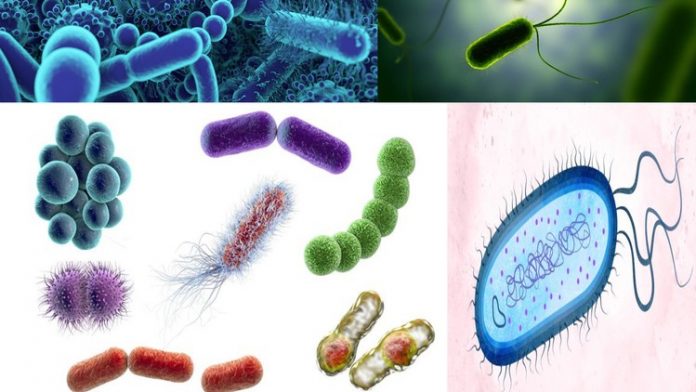
In this student will able to learn definition of bacteria, morphological classification of bacteria, applications of Bacteria. as we all know Bacteria are unicellular , free living , microscopic microorganisms capable of performing essential functions of life. They contain both DNA and RNA. They range from 0.2 to 2.0 um in diameter and 2-8 um in length. They are present in air, water ,soil . Food and all natural environment. An electron microscope is used for clear visualisation of internal structures of the bacteria.
Morphological classification of bacteria- Cocci: These types of bacteria are unicellular, spherical or elliptical shape.
Bacilli: – These are rod shaped or cylindrical bacteria which either remain singly or in pairs. Example: –Bacillus cereus.
Vibro: – The vibro are the curved, comma shaped bacteria and represented by a single genus. Example: – Vibro cholerae.
Spirilla: – These type of bacteria are spiral or spring like with multiple curvature and terminal flagella. Example: –Spirillum volutans.
Spirochetes : slender,flexious,spiral forms (Treponema).
Actinomycetes : branching filamentous bacteria. The shape is due to rigid cell wall.
Mycoplasmas: They are cell wall deficient bacteria and hence do not possess stable morphology. They occur in round or oval bodies with interlacing filaments.
On the basis of arrangement of bacterial cell:
Monococcus:– they are also called micrococcus and represented by single, discrete round Example: Micrococcus flavus.
Diplococcus:– the cell of the Diplococcus divides ones in a particular plane and after division, the cells remain attached to each other. Example: Diplococcus pneumonia.
Streptococcus: – here the cells divide repeatedly in one plane to form chain of cells. Example: – Streptococcus pyogenes.
Tetracoccus: – this consists of four round cells, which defied in two planes at a right angles to one another. Example: – Gaffkya tetragena.
Sarcina: -in this case the cells divide in three planes but they form a cube like configuration consisting of eight or sixteen cells but they have a regular shape. Example: –Sarcina lutea.
Applications of Bacteria– Production of enzymes, vaccines, sterilized product, Diagnosis of disease and treatment, Treatment of industrial waste material, Sterilization, Evaluation of disinfectant, Microbiological assays of antibiotics.








![Passive Income: Create & Sell Online Courses [Full Course]](https://oyoads.in/wp-content/uploads/passive-income-create-sell-online-courses-full-course_661cb1a9a14ff-218x150.jpeg)
![AI for Business Strategy & Planning [Masterclass]](https://oyoads.in/wp-content/uploads/ai-for-business-strategy-planning-masterclass_661cb19898162-218x150.jpeg)











![[100% Free]Python Bootcamp 2020 Build 15 working Applications and Games (31.5 Hours)](https://oyoads.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/Python-Bootcamp-2020-Build-15-working-Applications-and-Games-1-100x70.jpg)

![[100% Free]Java Programming: Complete Beginner to Advanced](https://oyoads.in/wp-content/uploads/2020/05/IMG_20200519_054150_522-100x70.jpg)
